MD® DrugScreen 5 Panel Drug Test Cup with 6 Adulterants 25/Box
Free FedEx Ground shipping on orders of $150 or more
Sales Tax Exempt? Call 800-915-7017 before ordering
Bulk discount rates
Below are the available bulk discount rates for each individual item when you purchase a certain amount
| Quantity | Per Item |
| 1 - 3 | $87.75 |
| 4 - 7 | $86.25 |
| 8 - 11 | $82.75 |
| 12+ | $79.50 |
Description
MD® DrugScreen 5 Panel Drug Test Cup with 6 Adulterants by American Drug Test
The MD® DrugScreen Five Panel Drug Test Cup is a fully integrated, self-contained drug test kit for detecting drugs and their metabolites in urine. This One-Step 5-panel urine drug test cup eliminates the handling of any urine, eliminates urine donor tampering, provides a unique approach for on-site drug testing, and is an accurate alternative to laboratory testing. With results in five minutes or less, time is saved by avoiding the typical 24 – 48 hour wait for results, as required by most laboratories. Our MD DrugScreen 5 Panel Drug Test Cup with 6 Adulterants is one of the most accurate tests available and is cost-effective, with Adulterants providing a safety net in which the 6 adulterant tests help to validate the urine sample. We offer highly competitive pricing – ideal for any budget- and with our bulk purchase pricing structure, the One Step Ten Panel Drug Test Cup is one of the most cost-effective products on the drug testing market today. Also, this test has a full 16 – 24 month shelf life, providing you with a greater opportunity to buy more and save. Our selection includes some of the most popular ten-panel drug tests. MD® DrugScreen 5 Panel Drug Test Cup with 6 Adulterants ensures sample integrity and provides accurate results in minutes with its all-in-one professional design.
FREE FedEx Ground Shipping in the USA
BULK PRICING - The more you buy, the more you save, and we will beat any 10-panel test cup pricing in the market
| 5 Panel Configurations (Choose Above) | ||
| Item Number | Drugs Tested | Adulterants |
| MDC-254AD | AMP, COC, MET, OPI, THC | OXI - Oxidants S.G. - Specific gravity pH - pH Level NIT - Nitrates GLUT - Glutaraldehyde CREA - Creatinine |
| MDC-354AD | COC, MET, OPI, OXY, THC | OXI - Oxidants S.G. - Specific gravity pH - pH Level NIT - Nitrates GLUT - Glutaraldehyde CREA - Creatinine |
| MDC-654AD | BZO, COC, MET, OPI, THC | OXI - Oxidants S.G. - Specific gravity pH - pH Level NIT - Nitrates GLUT - Glutaraldehyde CREA - Creatinine |
| Drug Detection Table in Urine | ||||
| Drug Name | Abbreviation | Cutoff | Detection Times * | Certifications |
| Amphetamines - Amphetamine and the structurally related “designer” drugs are sympathomimetic amines whose biological effects include potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulation, anorectic, hyperthermic, and cardiovascular properties. They are usually taken orally, intravenously, or by smoking. Amphetamines are readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and are then either deactivated by the liver or excreted unchanged in the urine with a half-life of about 12 hours. It can be detected in the urine for 1 to 2 days after use. Amphetamine is metabolized to deaminated (hippuric and benzoic acids) and hydroxylated metabolites. Methamphetamine is partially metabolized to amphetamine and its major active metabolite. Amphetamines increase the heart rate and blood pressure and suppress the appetite. Some studies indicate that heavy abuse may result in permanent damage to certain essential nerve structures in the brain. | AMP | 500 or 1000 ng/mL | 2 hours to 4 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Barbiturates - Barbiturates are a class of central nervous system depressants. They have a wide range of half-lives of 2 to 40 hours and can be detected in the urine for 1 to 4 days after use. Phenobarbital is a long-acting barbiturate derivative that has been used as a daytime sedative and very extensively as an anticonvulsant. Pentobarbital and secobarbital are two examples of short-acting barbiturate sedatives. Abuse of barbiturates can lead not only to impaired motor coordination and mental disorder but also to respiratory collapse, coma, and even death. Barbiturates are taken orally, rectally, or by intravenous or intramuscular injection. Short-acting barbiturates will generally be excreted in urine as metabolites, while the long-acting barbiturates will primarily appear unchanged. | BAR | 300 ng/ml | 2 hours to 3 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Benzodiazepines - Benzodiazepines are medications that are frequently prescribed for the symptomatic treatment of anxiety and sleep disorders. They produce their effects via specific receptors involving a neurochemical called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Because they are safer and more effective, Benzodiazepines have replaced barbiturates in the treatment of both anxiety and insomnia. Benzodiazepines are also used as sedatives before some surgical and medical procedures, and for the treatment of seizure disorders and alcohol withdrawal. | BZO | 300 ng/ml | 2 hours to 4 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Buprenorphine / Suboxone - Buprenorphine is a semi-synthetic opioid derived from thebaine, an alkaloid of the poppy Papaver somniferum. Buprenorphine is an opioid partial agonist. This means that, although Buprenorphine is an opioid, and thus can produce typical opioid effects and side effects such as euphoria and respiratory depression, its maximal effects are less than those of full agonists like heroin and methadone. At low doses, Buprenorphine produces sufficient agonist effect to enable opioid-addicted individuals to discontinue the misuse of opioids without experiencing withdrawal symptoms. The agonist effects of Buprenorphine increase linearly with increasing doses of the drug until it reaches a plateau and no longer continues to increase with further increases in dosage. This is called the "ceiling effect." Thus, Buprenorphine carries a lower risk of abuse, addiction, and side effects compared to full opioid agonists. In fact, Buprenorphine can actually block the effects of full opioid agonists and can precipitate withdrawal symptoms if administered to an opioid-addicted individual while a full agonist is in the bloodstream. This is the result of the high affinity Buprenorphine has to the opioid receptors. The affinity refers to the strength of attraction and the likelihood of a substance to bind with the opioid receptors. | BUP | 10 ng/ml | 2 hours to 3 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Cocaine - Cocaine, derived from leaves of the coca plant, is a potent central nervous system stimulant and a local anesthetic. Among the psychological effects induced by using cocaine are euphoria, confidence, and a sense of increased energy, accompanied by increased heart rate, dilation of the pupils, fever, tremors, and sweating. Cocaine is excreted in the urine primarily as benzoylecgonine in a short period of time. | COC | 150 or 300 ng/ml | 1 hour to 4 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Ecstasy - Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy) is a designer drug first synthesized in 1914 by a German drug company for the treatment of obesity. Those who take the drug frequently report adverse effects, such as increased muscle tension and sweating. MDMA is not clearly a stimulant, although it has, in common with amphetamine drugs, a capacity to increase blood pressure and heart rate. MDMA does produce some perceptual changes in the form of increased sensitivity to light, difficulty in focusing, and blurred vision in some users. Its mechanism of action is thought to be via the release of the neurotransmitter serotonin. MDMA may also release dopamine, although the general opinion is that this is a secondary effect of the drug (Nichols and Oberlender, 1990). The most pervasive effect of MDMA, occurring in virtually all people who took a reasonable dose of the drug, was to produce a clenching of the jaws. | MDMA | 500 ng/ml | 2 hours to 4 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Marijuana - Cannabinoid is a hallucinogenic agent derived from the flowering portion of the hemp plant. The active ingredients in Cannabinoids, THC & Cannabinol can be metabolized and excreted as 11-nor- Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-9carboxylic acid with a half-life of 24 hours. It can be detected for 1 to 5 days after use. Smoking is the primary method of use of Cannabinoids/cannabis. Higher doses used by abusers produce central nervous system effects, altered mood and sensory perceptions, loss of coordination, impaired short-term memory, anxiety, paranoia, depression, confusion, hallucinations, and increased heart rate. A tolerance to the cardiac and psychotropic effects can occur, and withdrawal syndrome produces restlessness, insomnia, anorexia, and nausea. | THC | 50 ng/ml | 2 hours to 4 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Methadone - Methadone is a synthetic analgesic drug that is originally used in the treatment of narcotic addicts. Among the psychological effects induced by using methadone are analgesia, sedation, and respiratory depression. An overdose of methadone may cause coma or even death. It is administered orally or intravenously and is metabolized in the liver and excreted in urine as methadone, EDDP, EMDA, and methanol. The kidneys are a major route of methadone excretion. Methadone has a biological half-life of 15 to 60 hours. | MTD | 300 ng/ml | 3 hours to 3 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Methadone Metabolite - Test for the qualitative determination of EDDP (2-ethylidene-1,5-dimethyl-3,3-diphenylpyrrolidine) in human urine at a Cut-Off concentration of 300 ng/mL. The benefit of measuring EDDP instead of methadone is that individuals in methadone programs sometimes divert their methadone into the illicit drug market and then spike their urine sample with a small quantity of methadone to cover the diversion. Their urine sample may test positive for methadone, but would not test positive for EDDP. | EDDP | 300 ng/ml | 1 hour to 3 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Methamphetamines - Methamphetamine is a potent sympathomimetic agent with therapeutic applications. Acute higher doses lead to enhanced stimulation of the central nervous system and induce euphoria, alertness, and a sense of increased energy and power. More acute responses produce anxiety, paranoia, psychotic behavior, and cardiac dysrhythmias. The pattern of psychosis, which may appear at a half-life of about 15 hours and is excreted in urine as amphetamine and oxidized as deaminated and hydroxylated derivatives. However, 40% of methamphetamine is excreted unchanged. Thus, the presence of the parent compound in the urine indicates methamphetamine use. | mAMP | 500 or 1000 ng/ml | 2 hours to 4 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Morphine / Opiates - The opiates, such as heroin, morphine, and codeine, are derived from the resin of the opium poppy. The principal metabolites of opiates are morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide, normorphine, and codeine, with a half-life of about 3 hours. Heroin is quickly metabolized to morphine. Thus, morphine and morphine glucuronide might both be found in the urine of a person who has taken only heroin. The body also changes codeine to morphine. Thus, the presence of morphine (or the metabolite, morphine glucuronide) in the urine indicates heroin, morphine, and/or codeine use. The test for Morphine (MOP) of the Multi-Drug Urine Test Panel yields a positive result when the morphine in urine exceeds 300ng/mL. | MOP / OPI | 300 or 2000 ng/mL | 2 hours to 3 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Oxycodone - Oxycodone is known as OxyContin and Roxicodone. It is an ingredient of Percodan, Percocet, Roxicet, and Tylox. Oxycodone is a semi-synthetic opiate derived from opium. Like other opiates, Oxycodone is characterized by its analgesic properties and the tendency for users to form a physical dependency and develop tolerance with extended use. Oxycodone is usually administered in combination with non-opiate analgesics such as acetaminophen and salicylates for the relief of moderate to severe pain. Oxycodone is a central nervous system depressant that may cause drowsiness, dizziness, lethargy, weakness, and confusion. Toxicity in an overdose of Oxycodone can lead to stupor, coma, muscle flaccidity, severe respiratory depression, hypotension, and cardiac arrest. Oxycodone is metabolized by N- and O-demethylation. One of the metabolites, oxymorphone, is a potent narcotic analgesic, while the other, nor oxycodone, is relatively inactive. Between 33 to 61% of a single dose of Oxycodone is excreted in a 24-hour urine collection and consists of 13-19% free Oxycodone, 7-29% glucuronide conjugated Oxycodone, 13-14% glucuronide conjugated oxymorphone, and an unknown amount of nor oxycodone. The detection time window of Oxycodone is 1-3 days following use. | OXY | 100 ng/ml | 1 hour to 2 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Phencyclidine - Phencyclidine is an arylcyclohexylamine that was originally used as an anesthetic agent and a veterinary tranquilizer. Phencyclidine can produce hallucinations, lethargy, disorientation, loss of coordination, trance-like ecstatic states, a sense of euphoria, and visual distortions. It has many street names, such as “angel dust” and “crystal cyclone,” etc. Phencyclidine can be administered orally, by nasal ingestion, smoking, or by intravenous injection. It is metabolized in the liver and excreted through the kidneys in urine in unchanged form and oxidized metabolites with a half-life of about 12 hours. Suction and urinary acidification in the treatment of overdose typically reduce its half-life from three days to one day. | PCP | 25 ng/ml | 4 hours to 14 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Propoxyphene - This test will be positive if the sample tested contains at least 300 nanograms of propoxyphene or norpropoxyphene. Propoxyphene is a prescription drug for the relief of pain. Propoxyphene hydrochloride (Darvon, Dolene, and others) is available in 32mg and 65mg capsules; propoxyphene napsylate (Darvon-N) is available in 100mg tablets or as a suspension. It is structurally related to methadone. | PPX | 300 ng/ml | 1 hour to 3 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| Tricyclic Antidepressants / Nortriptyline - chemical compounds used primarily as antidepressants discovered in the early 1950s. The first TCA reported for the treatment of depression was imipramine, used primarily in the clinical treatment of mood disorders such as major depressive disorder (MDD). Tricyclic antidepressants are possibly more effective in treating melancholic depression than other antidepressant drug classes. | TCA | 1000 ng/ml | 8 hours to 7 days | FDA 510(k) CLIA Waived |
| * Detection times are not guaranteed. This assay provides only a preliminary analytical test result. A more specific alternate chemical method must be used in order to obtain a confirmed analytical result. Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS) is the preferred confirmatory method. Clinical consideration and professional judgment should be applied to any drug of abuse test result, particularly when preliminary positive results are indicated. |
||||
5 Panel Drug Test Procedure In Just Five Easy Steps
- Have the donor provide a urine sample in the 10-panel drug test cup up to the level between the Max line and the Min. line urine level.
- Securely tighten the cap and verify the range in the temperature strip. This provides a level of security that the urine is fresh from the donor.
- Remove the front label to view the results.
- Compare the adulteration test strips to the enclosed color chart. This provides a second layer of security to avoid adulteration or tampering of the urine sample.
- Read the results following the sample image below.
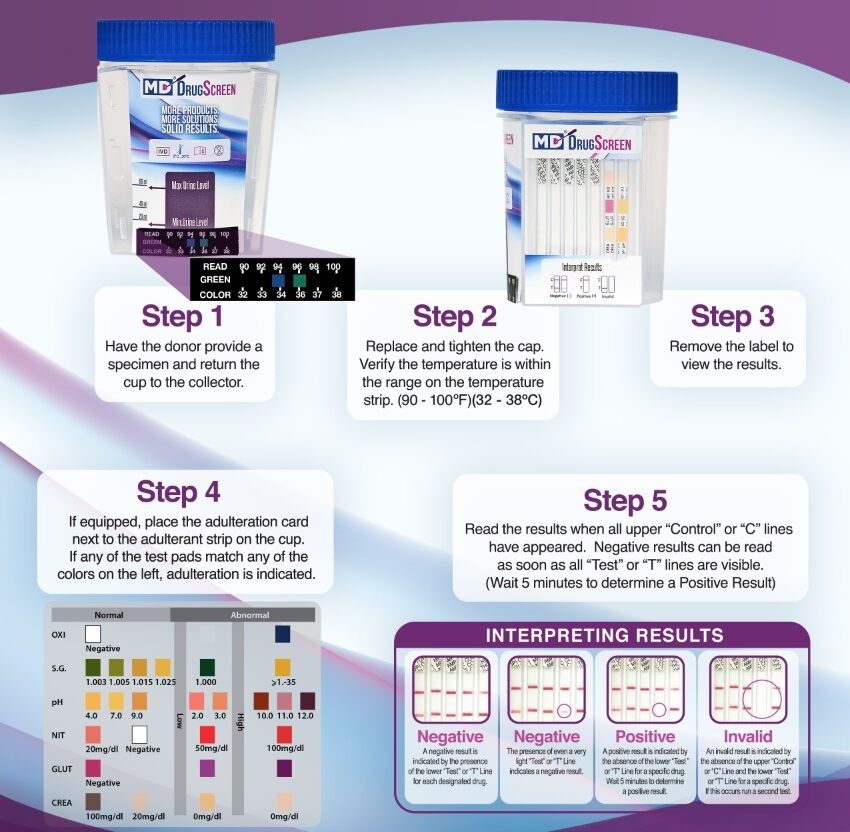
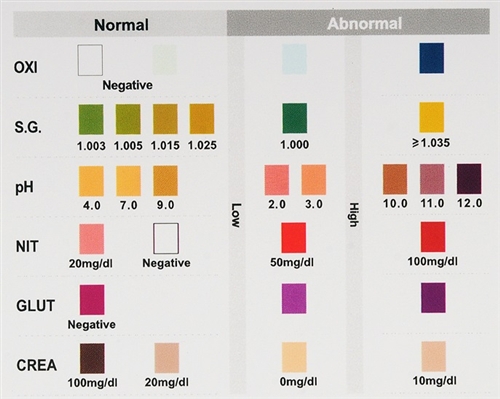
Adulterant Interpretation
Oxidants (OXI): Tests for the presence of oxidizing agents such as bleach and peroxide in the urine.
Specific Gravity (S.G.): Tests for sample dilution. Normal levels for specific gravity will range from 1.003 to 1.030. Specific gravity levels of less than 1.003 or higher than 1.030 may be an indication of adulteration or specimen dilution.
pH Level (pH): Tests for the presence of acidic or alkaline adulterants in urine. Normal pH levels should be in the range of 4.0 to 9.0. Values below pH 4.0 or above 9.0 may indicate the sample has been altered.
Nitride (NIT): Tests for commercial adulterants such as Klear and Whizzies. Normal urine specimens should contain no trace of nitride. Positive results for nitride usually indicate the presence of an adulterant.
Glutaraldehyde (GLUT): Tests for the presence of an aldehyde. Glutaraldehyde is not normally found in a urine specimen. Detection of glutaraldehyde in a specimen is generally an indicator of adulteration.
Creatinine (CREA): Tests for the specimen of dilution and flushing. Normal creatinine levels are between 10 mg/dl and 300 mg/dl. Low creatinine (less than 5 mg/dl) may indicate a diluted urine specimen.