Learning Center
Drug Testing Facts
Drug testing is the evaluation of a urine, saliva, hair, blood or other type of biological sample to determine if the subject has been using the drug or drugs in question. There are many circumstances that may lead to drug testing:
- Pre-employment drug screening test or random, work-related drug testing to identify on-the-job drug abuse.
- College or professional athletic drug testing.
- Post-accident vehicular or job related drug testing which may have involved human error resulting in casualties or property damage.
- Safety-related drug testing - if an employee's job could lead to safety issues if judgement or physical ability were impaired.
Drug testing is often done when applying for employment, especially for positions that may involve federal transportation, airline industries, railways, hospitals, and other workplaces where public safety is of the utmost importance. However, workplace drug testing is now common in general for many U.S. employers to lessen the impact from drug abuse, safety concerns, and low productivity in the workplace.
Document Library
![]() Cross Reactivity Guide for Urine Drug Tests
Cross Reactivity Guide for Urine Drug Tests
![]() Abbott Diagnostics (Alere) Cross Reaction Guide for Urine Drug Tests
Abbott Diagnostics (Alere) Cross Reaction Guide for Urine Drug Tests
![]() Natural & Synthetic Opiates Chart
Natural & Synthetic Opiates Chart
Abbreviations, Detection Times and Cutoff Levels
Listed below are the most common drug abbreviations, detection times, and cutoff levels used for point-of-care rapid drug and alcohol screening products. Please note that although most of the abbreviations are universal there are a few that differ slightly depending on the manufacturer of the test device. For example, mAMP=MET, MOP=OPI300 and FEN=FYL. Please contact us if you need clarification on anything or if you need additional cutoff levels that are not listed.
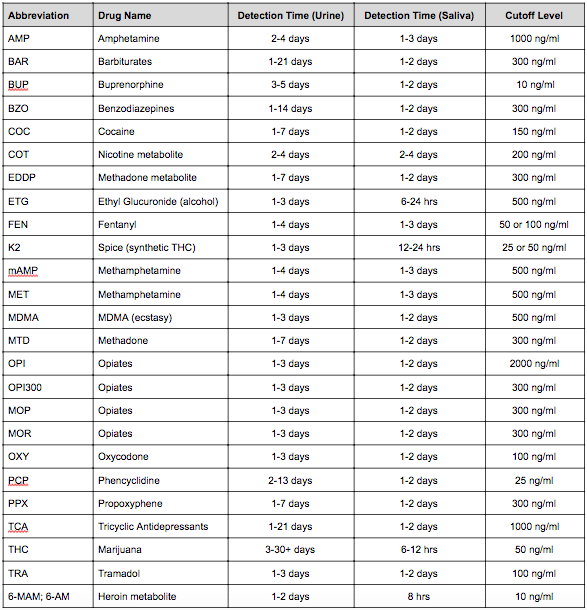
| SALIVA & URINE DRUG DETECTION TIMES AND CUT-OFF LEVELS* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug Name | Abbreviation | Cut Off Level | Approximate Urine Detection Times | Approximate Saliva Detection Times |
| Amphetamine | AMP | 1000 ng/ml | 2-4 Days | 1-3 Days |
| Amphetamine 300 | AMP-300 | 300 ng/ml | 2-4 Days | 1-3 Days |
| Amphetamine | AMP-50 | 50 ng/ml | 2-4 Days | 1-3 Days |
| Barbiturates | BAR | 300 ng/ml | 3-10 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Barbiturates | BAR-60 | 60 ng/ml | 3-10 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Benzodiazepine | BZO | 300 ng/ml | 1-7 Days * | 1-2 Days |
| Benzodiazepine | BZO-30 | 30 ng/ml | 1-7 Days | 1-2 Days * |
| Buprenorphine | BUP | 10 ng/ml | 3-5+ Days | 1-2 Days |
| Buprenorphine | BUP-5 | 5 ng/ml | 3-5+ Days | 1-2 Days |
| Cocaine | COC | 300 ng/ml | 1-7 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Cocaine 150 | COC-150 | 150 ng/ml | 1-7 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Cocaine | COC-20 | 20 ng/ml | 1-7 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Cotinine (Nicotine Metabolite) | COT | 200 ng/ml | 2-4 Days | 2-4 Days |
| Ecstasy Methylenedioxymethamphetamine | MDMA | 500 ng/ml | 1-3 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Ecstasy Methylenedioxymethamphetamine | MDMA-100 | 100 ng/ml | 1-3 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Methadone Metabolite | EDDP | 300 ng/ml | 1-7 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Marijuana Tetrahydrocannabinol | THC | 50 ng/ml | 3-15 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Marijuana Tetrahydrocannabinol | THC-25 | 25 ng/ml | 3-15 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Methadone | MTD | 300 ng/ml | 1-7 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Methadone | MTD-30 | 30 ng/ml | 1-7 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Methamphetamine | mAMP, MET | 1000 ng/ml | 1-4 Days | 1-3 Days |
| Methamphetamine 500 | mAMP-500, MET-500 | 500 ng/ml | 1-4 Days | 1-3 Days |
| Methamphetamine | MET-50 | 50 ng/ml | 1-4 Days | 1-3 Days |
| Morphine | MOP, MOR, MOP-300 | 300 ng/ml | 1-3 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Opiates OPI | OPI | 2000 ng/ml | 1-3 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Opiates | OPI-40 | 40 ng/ml | 1-3 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Oxycodone | OXY | 100 ng/ml | 1-3 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Oxycodone | OXY-20 | 20 ng/ml | 1-3 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Phencyclidine | PCP | 25 ng/ml | 2-30 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Propoxyphene | PPX | 300 ng/ml | 1-7 Days | 1-2 Days |
| Tricyclic Antidepressants | TCA | 1000 ng/ml | 1-14 Days * | 1-2 Days |
| * Note: The above chart gives approximate detection periods for each substance by test type. The range depends on amount and frequency of use, metabolic rate, body mass, age, overall health, drug tolerance, and urine pH. Click Here for Detailed Information Guide on Detection Times per Drug Class |
||||
Adulterants in Drug Testing
The verb “adulterate” is defined as “rendering something poorer in quality by adding another substance, typically an inferior one.” This activity is illicit where drug testing is concerned, as the process of tampering with a drug test sample can alter the results, rendering them invalid and ineffectual. To reduce or eliminate adulterants in drug testing at your organization, you will need to combat it from both sides: prevention before the fact and detection afterwards. In addition, it never hurts to understand how people try to tamper with drug test results, as their methods can guide your strategies for prevention and detection.
